Implementing Cisco SD-WAN and Palo Alto Prisma SASE Together: A Real-World Implementation Guide
The Perfect Storm: Why SD-WAN + SASE Makes Sense
If you've been following my previous posts on SD-WAN fundamentals and SASE/SSE implementation strategies, you're aware that both technologies address critical gaps in traditional network architectures. But what happens when you need both?
For many mid-sized organizations, the reality is that SD-WAN and SASE aren't competing solutions – they're complementary technologies that, when implemented together, create a robust, scalable, and secure network foundation for the modern enterprise.
Let me walk you through a real-world scenario: implementing Cisco SD-WAN and Palo Alto Prisma SASE for a 75-office organization that needed to modernize its entire WAN and security infrastructure simultaneously. This framework applies to any vendor combo, I just selected Cisco SD-WAN and Palo Alto SASE because they’re a leader in their respective spaces
The Business Case: Why This Company Chose Both
The Starting Point
Our example organization is a regional healthcare chain with:
75 locations across multiple states
Mix of large hospitals, small e-care, and back offices
Legacy MPLS network struggling with bandwidth limitations
Outdated firewall infrastructure at each location
Growing cloud adoption is creating security blind spots
Remote work requirements post-pandemic
Aggressive expansion plans requiring rapid site deployment
The Challenge: Solving Multiple Problems Simultaneously
Traditional approaches would tackle these challenges sequentially:
First, replace the WAN infrastructure (SD-WAN)
Then, modernize security (SASE)
Finally, optimize for cloud and remote access
But this sequential approach creates problems:
Extended timelines with multiple vendor engagements
Temporary security gaps during transitions
Increased complexity in managing parallel projects
Higher costs from multiple infrastructure refreshes
The Solution: Integrated SD-WAN + SASE Deployment
By implementing Cisco SD-WAN and Palo Alto Prisma SASE together, this organization could:
Modernize WAN and security infrastructure simultaneously
Create consistent security policies across all locations
Enable secure direct cloud access from branches
Support remote workers with the same security posture
Reduce total project timeline and implementation costs
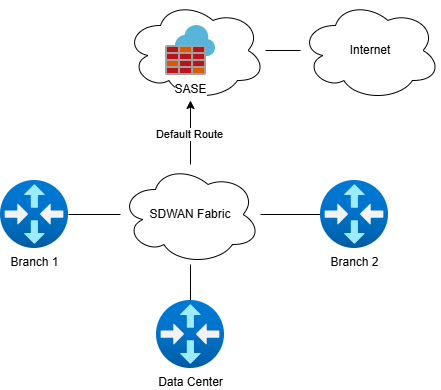
Architecture Overview: How They Work Together
The Integration Model
Cisco SD-WAN Foundation:
Centralized policy management through vManage
Dynamic path selection and traffic steering
Application-aware routing and QoS
Secure fabric connectivity between sites
Palo Alto Prisma SASE Layer:
Cloud-delivered security services
Secure web gateway and CASB functionality
Zero Trust Network Access for remote users
Consistent security policy enforcement
Key Integration Points
1. Traffic Steering Integration:
2. Policy Coordination:
SD-WAN handles path selection and WAN optimization
SASE provides security inspection and policy enforcement
Coordinated policies ensure traffic reaches both systems appropriately
3. Centralized Management:
vManage for SD-WAN orchestration
Prisma Access for SASE policy management
Integration APIs for coordinated policy deployment
Implementation Strategy: A Phased Approach
Phase 1: Foundation and Planning (Months 1-2)
Infrastructure Assessment:
Current WAN utilization and performance analysis
Security posture evaluation and gap analysis
Application flow mapping and criticality assessment
Bandwidth requirements and growth projections
Design and Architecture:
Hub site identification and design
Branch site categorization (large, medium, small)
Internet breakout strategy definition
Security policy framework development
Team Preparation:
Technical training on both platforms
Vendor partner engagement and support planning
Change management and communication planning
Pilot site selection and success criteria definition
Phase 2: Hub Sites and Pilot Implementation (Months 2-4)
Hub Site Deployment:
Install Cisco vEdge routers at data centers
Deploy vManage controllers and vSmart controllers
Configure SASE cloud gateways and policies
Establish a secure fabric between hubs
Pilot Branch Implementation:
Select 3-5 representative branch locations
Install vEdge devices with appropriate sizing
Configure Prisma Access client connections
Test application performance and security policies
Key Success Metrics:
Application response time improvements
Security policy enforcement validation
Failover and redundancy testing results
User experience feedback from pilot locations
Phase 3: Branch Rollout (Months 4-8)
Systematic Branch Deployment:
Tier 1 sites (largest/most critical): Months 4-5
Tier 2 sites (medium locations): Months 5-7
Tier 3 sites (smallest locations): Months 7-8
Per-Site Implementation Process:
Pre-staging equipment configuration
Coordinated installation during maintenance windows
Parallel operations with legacy systems during testing
Cutover and legacy system decommissioning
Post-implementation optimization and tuning
Phase 4: Remote Access and Mobile Users (Months 6-8)
Prisma Access GlobalProtect Deployment:
Client software packaging and deployment
User authentication integration (Active Directory/SSO)
Mobile device management integration
Policy refinement based on user behavior analytics
Technical Implementation Details
Cisco SD-WAN Configuration Highlights
vManage Policy Configuration:
# Application-aware routing for cloud traffic
policy:
application_routing:
- name: "Office365_Direct"
applications: ["office365", "teams", "sharepoint"]
action: "direct_internet"
sla_class: "realtime"
- name: "Critical_Apps_MPLS"
applications: ["erp", "pos_system"]
action: "mpls_preferred"
sla_class: "business_critical"Traffic Steering for SASE Integration:
# Route specific traffic to SASE inspection
route_policy:
- name: "SASE_Steering"
match:
- destination: "0.0.0.0/0"
- protocol: ["http", "https"]
action:
- next_hop: "prisma_gateway"
- backup_path: "direct_internet"Palo Alto Prisma SASE Configuration
Security Policy Framework:
# Branch office security profile
security_rules:
- name: "Branch_Internet_Access"
source: ["branch_users"]
destination: ["internet"]
services: ["web_browsing", "ssl"]
action: "allow"
profiles:
- threat_prevention: "strict"
- url_filtering: "corporate_policy"
- file_blocking: "standard"
- data_filtering: "pci_compliance"Zero Trust Access Policies:
# Remote access security policies
ztna_policies:
- name: "Remote_App_Access"
users: ["authenticated_users"]
applications: ["internal_web_apps"]
conditions:
- device_compliance: "required"
- multi_factor_auth: "required"
access: "allow"Integration Challenges and Solutions
Challenge 1: Traffic Flow Optimization
Problem: Ensuring traffic reaches both SD-WAN and SASE systems without creating performance bottlenecks or routing loops.
Solution: Implemented service chaining approach:
SD-WAN handles initial routing decisions
SASE provides security inspection for internet-bound traffic
Direct internal traffic bypasses SASE for performance
Application-specific routing policies optimize flow paths
Challenge 2: Policy Consistency
Problem: Maintaining consistent security policies across SD-WAN direct internet breakouts and SASE-inspected traffic.
Solution: Developed a unified policy framework:
Centralized policy definition in the security team
Automated policy translation for both platforms
Regular policy synchronization and compliance checking
Exception handling for performance-critical applications
Challenge 3: Operational Complexity
Problem: Managing two separate platforms with different management interfaces and operational procedures.
Solution: Created operational integration:
Cross-platform monitoring dashboards
Unified incident response procedures
Coordinated change management processes
Integrated reporting and analytics
Challenge 4: Performance Optimization
Problem: Balancing security inspection depth with application performance requirements.
Solution: Implemented tiered inspection approach:
Full SASE inspection for high-risk traffic
Lightweight inspection for trusted applications
Direct routing for performance-critical internal traffic
Dynamic policy adjustment based on performance metrics
Real-World Results and Lessons Learned
Quantifiable Improvements
Network Performance:
40% improvement in application response times
60% reduction in WAN costs through MPLS optimization
99.9% uptime achievement across all locations
50% faster new site deployment process
Security Posture:
90% reduction in security incidents
100% visibility into cloud application usage
Consistent policy enforcement across all locations
Comprehensive threat intelligence integration
Operational Efficiency:
70% reduction in network management overhead
Centralized troubleshooting and monitoring
Automated policy deployment and compliance
Simplified vendor management relationships
Key Lessons Learned
1. Start with Strong Design Foundations. The success of the integration depended heavily on upfront architectural planning. Time invested in understanding traffic flows and application requirements paid dividends throughout implementation.
2. Pilot Testing is Critical. The pilot phase revealed integration issues that would have been costly to discover during full rollout. Testing both normal operations and failure scenarios was essential.
3. Team Training Makes the Difference Having team members trained on both platforms enabled faster troubleshooting and more efficient operations. Cross-platform expertise was more valuable than deep specialization in either technology alone.
4. Vendor Coordination is Essential. Regular coordination between Cisco and Palo Alto support teams prevented finger-pointing during issues and accelerated problem resolution.
Cost Considerations and ROI Analysis
Implementation Costs
NOTE: These are just round numbers for the sake of the example. Numbers will obviously vary depending on the environment.
Cisco SD-WAN Investment:
vEdge hardware for 75 locations: $450,000
Licensing and support (3 years): $275,000
Professional services and implementation: $150,000
Total SD-WAN Investment: $875,000
Palo Alto Prisma SASE Investment:
Cloud service licensing (3 years): $380,000
GlobalProtect licensing for 2,000 users: $120,000
Professional services and integration: $100,000
Total SASE Investment: $600,000
Combined Implementation: $1,475,000
Cost Savings and ROI
Annual Operational Savings:
MPLS cost reduction: $400,000/year
Reduced firewall hardware refresh: $150,000/year
Operational efficiency gains: $200,000/year
Total Annual Savings: $750,000
3-Year ROI Calculation:
Total savings over 3 years: $2,250,000
Net ROI: $775,000 (53% return on investment)
Payback period: 23 months
Best Practices for Similar Implementations
Technical Best Practices
1. Application Flow Mapping
Document all application flows before implementation
Identify performance-critical applications requiring special handling
Plan traffic steering policies to optimize both security and performance
2. Gradual Traffic Migration
Implement parallel operations during cutover
Use canary deployments for policy changes
Maintain rollback procedures for each phase
3. Monitoring Integration
Implement unified monitoring across both platforms
Create cross-platform correlation for troubleshooting
Establish performance baselines before and after implementation
Organizational Best Practices
1. Cross-Functional Team Formation
Include networking, security, and application teams in planning
Establish clear roles and responsibilities for each platform
Create escalation procedures for complex issues
2. Change Management
Communicate benefits and changes to end users
Provide training for help desk and support teams
Establish feedback mechanisms for continuous improvement
3. Vendor Relationship Management
Establish joint vendor support procedures
Regular vendor coordination meetings during implementation
Clear escalation paths for integration issues
Future Considerations and Evolution
Technology Roadmap Integration
Short-term Enhancements (6-12 months):
Advanced analytics integration between platforms
Automated policy optimization based on usage patterns
Enhanced zero-trust capabilities for internal applications
Medium-term Evolution (1-2 years):
AI-driven security policy optimization
Enhanced cloud integration and multi-cloud support
Advanced automation and orchestration capabilities
Long-term Strategy (2+ years):
Full SASE convergence as technologies mature
Edge computing integration for distributed applications
Advanced threat intelligence and behavioral analytics
Scalability Planning
The integrated architecture supports future growth through:
Cloud-native scaling for SASE services
Modular SD-WAN expansion for new locations
Consistent policy framework for diverse site types
Automated onboarding for rapid site deployment
Conclusion: The Power of Integrated Implementation
Implementing Cisco SD-WAN and Palo Alto Prisma SASE together created more value than either technology could deliver independently. The integration enabled this mid-sized organization to:
Modernize their entire network and security infrastructure simultaneously
Achieve better performance and security outcomes than sequential implementation
Reduce total project timeline and costs through coordinated deployment
Create a foundation for future growth and technology evolution
For organizations considering similar implementations, the key success factors are:
Comprehensive upfront planning and design
Strong vendor coordination and support
Phased implementation with thorough testing
Investment in team training and development
Focus on operational integration, not just technical integration
The result is a modern, secure, and scalable network infrastructure that supports business growth while reducing operational complexity and costs.
Want to learn more about the individual technologies? Check out my previous posts on SD-WAN fundamentals and implementation strategies and SASE/SSE evaluation and deployment guidance for deeper dives into each technology area.
Considering a similar implementation in your organization? I'd love to hear about your experiences with SD-WAN and SASE integration. Connect with me on LinkedIn or drop a comment below to share your challenges, successes, and lessons learned!